Mind Those URLs: How to Create an SEO-Friendly Website Structure

This might seem like a no-brainer, but it’s important to ensure that your web pages are logically organized. Doing this does more than simply help your website’s users navigate around more easily — it does the same for search engines. In short, the way you organize your site’s pages can help you rank higher in search engines and drive more traffic to your website.
Fortunately, structuring (or restructuring) your website’s architecture doesn’t have to be a chore. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at website structure and discuss why it’s important for Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Then, we’ll guide you through how to create an SEO-friendly website structure. Let’s get started!
An Introduction to Website Architecture
Website structure (also known as website architecture) refers to the way your content is categorized and linked together. Essentially, it concerns your site’s framework and the organization of your pages.
For instance, most websites group their pages by subject or topic. In the example below, you can see that pages are organized under appropriate headings:
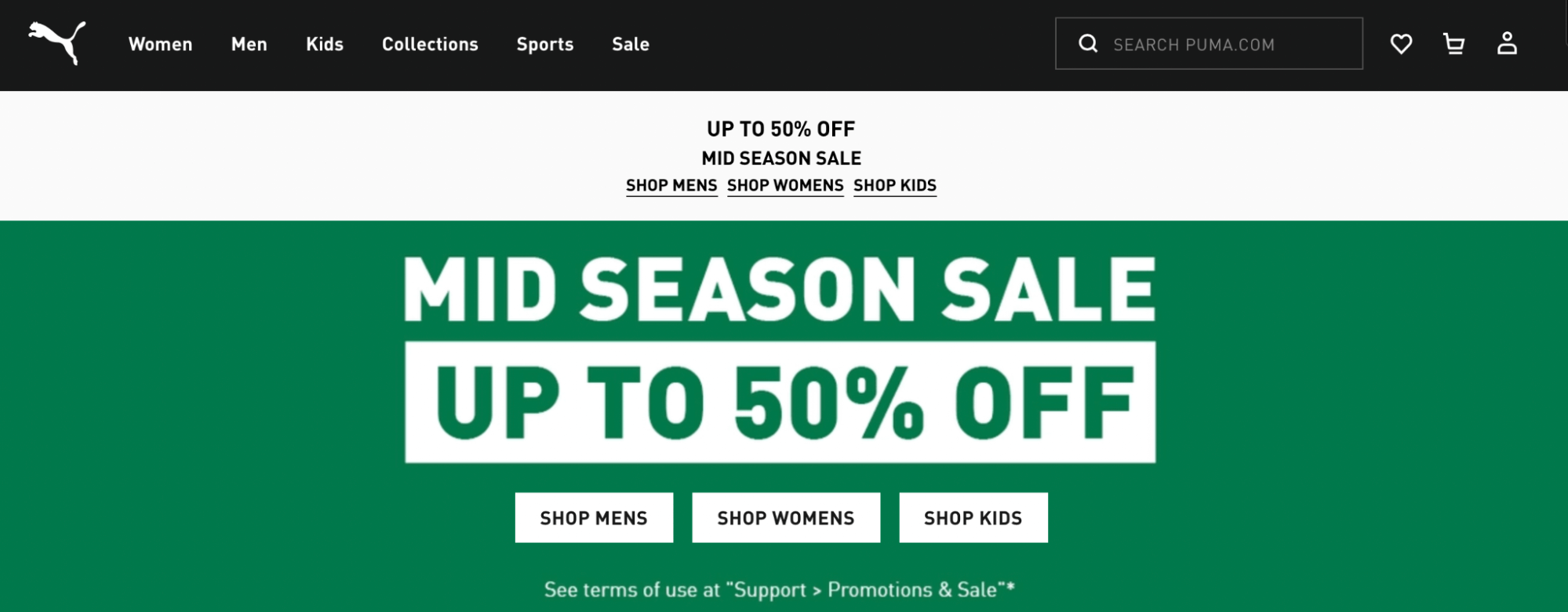
These headings often branch off into more specific subcategories. As you can see, the Sports page contains links to other lower-tier pages such as Explore Football and Modest Activewear:
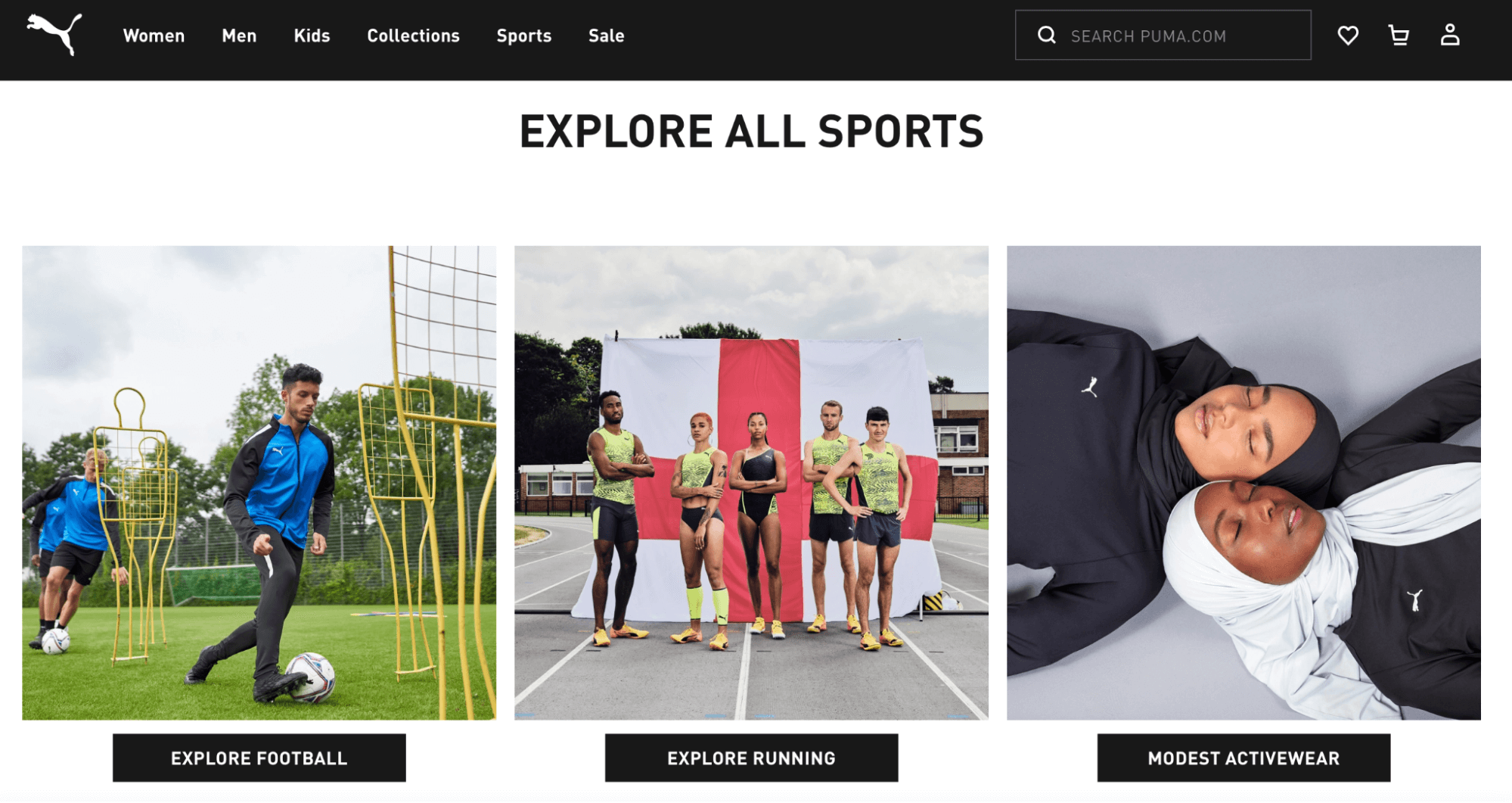
A good website structure enables users to navigate your site intuitively, guiding them toward an intended goal. Additionally, it helps search engines understand your website better and enables them to differentiate between your pages.
Why Website Structure is Important for SEO
One of the main reasons why web structure is important for SEO is because it helps search engines find and index your pages. If you have pages that are several clicks away from your home page, it’s hard for search engines to access them.
Not only that, but it also enables users to easily navigate your content. With good site structure, your target audience can quickly find what they need:
This can help keep users on your site for longer, reducing your bounce rate. Google will see this as a sign that your website provides value, and in turn, it can improve your visibility in search results.
Additionally, good web structure prevents cannibalization. When you organize your site, your content has distinct goals and topics that are instantly identifiable to search engines. Therefore, even if you cover similar topics across multiple pages, your structure makes it so that your pages aren’t ranking for the same keywords.
How to Create an SEO-Friendly Website Structure
Now that you know a bit more about web structure and why it’s important, let’s take a look at some specific ways to create an SEO-friendly structure for your website.
Establish a Simple Hierarchy
It’s a good idea to design a site with multiple categories that also branch off into organized subpages. This makes it easy for users (and search engines) to navigate your content. It also enables them to engage with your top-tier pages first (which are often your most important ones).
With a complicated site structure, it’s hard for users to find what they need. Therefore, consider designing your site so that visitors can quickly find what they’re looking for, no matter where they land on your site.
Creating a simple hierarchy is also important for SEO. Clear categories and internal links make your content easier to crawl.
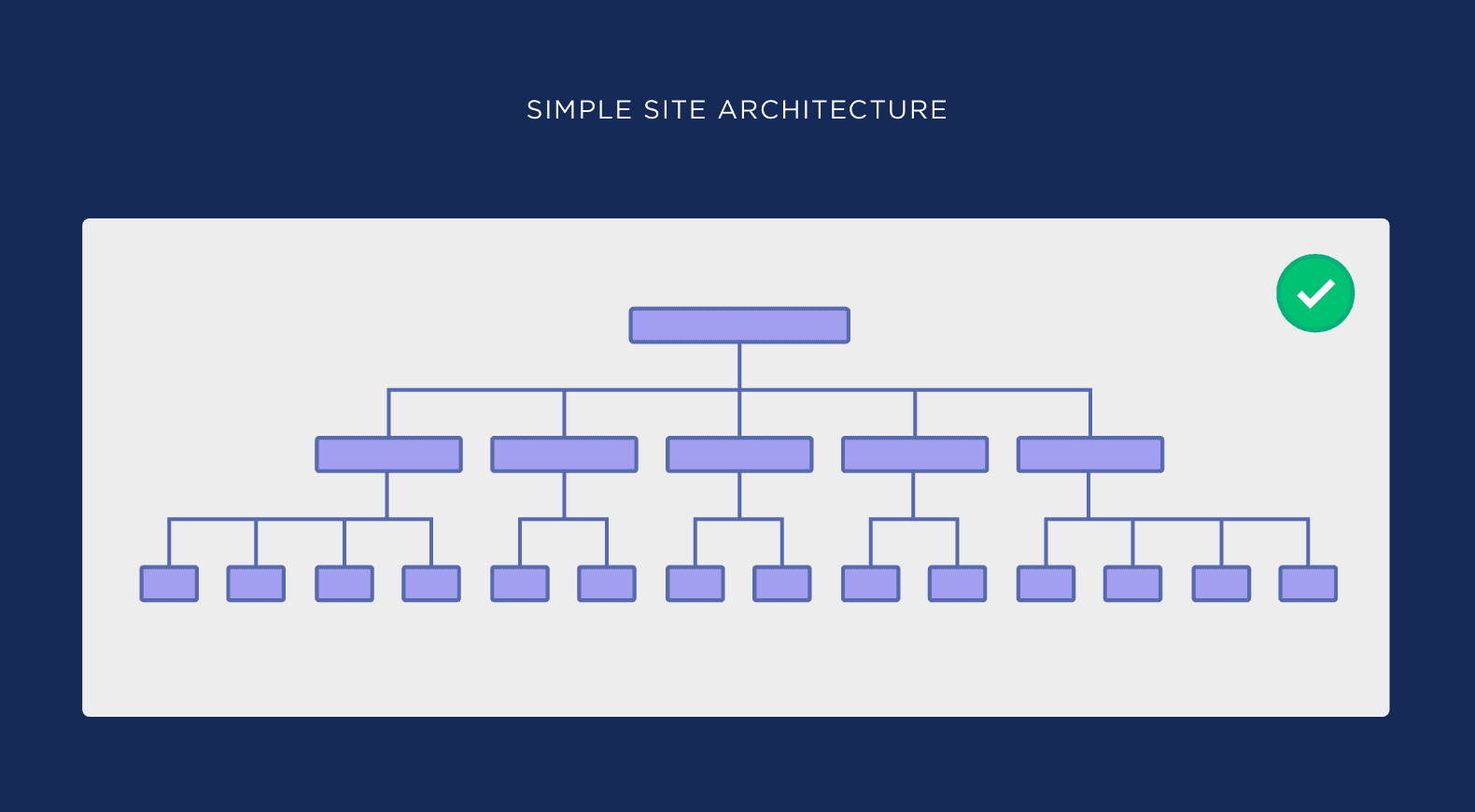
Image Credit: Backlinko
Organize Subpages into Logical Categories
As we’ve mentioned earlier, categories add organization and structure to your pages. Without them, your content can be difficult to navigate.
Better yet, categories don’t have to be set in stone. For instance, you might add a new page to an existing category. Or, if you design new pages that don’t fit into your categories, you can easily create new ones for them.
If you manage an e-commerce store, you might consider using product categories. If you run a blog, you might organize content according to topics:
A poorly organized site that lacks defined places for different types of content can also be prone to keyword overlaps. Then, you’re more at risk of facing duplication and keyword cannibalization issues.
Get Content Delivered Straight to Your Inbox
Subscribe to our blog and receive great content just like this delivered straight to your inbox.
Use Internal Links to Your Advantage
Since your site structure is heavily determined by the way your pages are grouped together, your navigation menu becomes very important. Here, you can show users where to find your main content and subcategories.
However, you can also use internal links on your posts, directing visitors to other relevant articles. For instance, you might present users with similar travel guides, using descriptive anchor text:

By linking several pieces of content that cover different aspects of the same topic, you can help search engines recognize your site as an industry expert. This authority can be hard to achieve if your pages are scattered randomly with no obvious relationship to one another.
Include Relevant Keywords
When choosing keywords for your content, you’ll need to consider search volume and traffic potential. Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, and Ahrefs are excellent tools that enables you to find relevant keywords and judge how easy/difficult it is to rank for them:
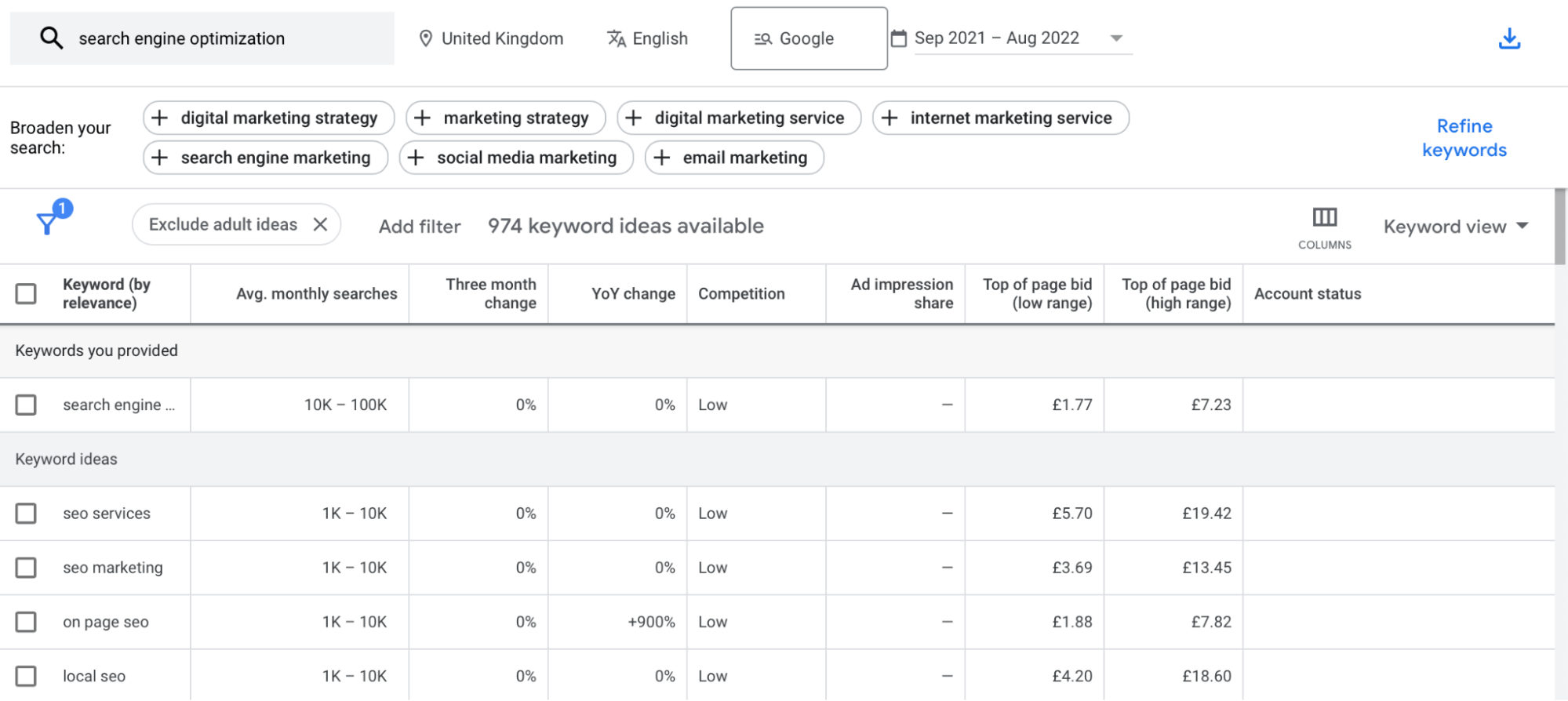
It’s important to pay attention to how competitive keywords are. Your chances of outranking high-traffic websites are slim. Therefore, you might want to opt for long-tail keywords. These have a lower search volume but are easier to rank for since they’re more specific.
Once you’ve chosen your keywords, you can place them in optimal spots like your URLs, titles, and meta descriptions:

You can also incorporate these search terms into your content. However, you’ll want to avoid keyword stuffing, since this can make your content seem unnatural.
Create “Pillar” Pages
Think of pillar pages like really comprehensive, important pieces of content. You can create pillar pages that cover broader subject areas. Then, you can use these pages to link to more in-depth, specific content. That way, you can highlight your most important content and position your pillar pages to rank for high-volume keywords.
However, you can also pull visitors further into your site by using long-tail keywords for your lower-level pages:
This way, users searching for more specific content can easily bypass pillar pages to access what they need. Meanwhile, your hub pages can cater to those looking for general information.
Optimize URL Structure
Search engines also use your URL to comprehend your page content. In fact, they consider many factors including on-page and off-page elements.
And when we discuss simple hierarchy and organizing content using categories above, this is what we’re talking about! URL structure is the primary means in which we organize content.
Permalink best practices suggest that you keep URLs short and make use of your targeted keywords. Additionally, consider using lowercase letters and joining words together with hyphens.
A well-executed site structure will typically have SEO-friendly URLs that show subpages organized and nested within logical parent “categories,” or subfolders.

This enables you to describe how your subtopics relate to your general pages. Plus, it shows visitors where they are within your site.
Boost Your Site Speed
Website speed is a crucial indicator of a user-friendly website. In fact, as page load time goes from 1 to 3 seconds, the bounce rate increases by 32%. However, site speed also affects how search engines read your website. The longer they take to crawl your pages, the lower you’re likely to rank.
With a fast website, Google can crawl multiple pages at once. Therefore, it’s important to test your site speed with a free tool like Pingdom:
There are many factors that can affect your web performance, such as user location, browser type, and your hosting server. As such, making the switch to managed WordPress hosting can be a good decision:

At DreamHost, you can expect top-of-the-range speeds with built-in caching, available with all plans. However, with our Plus and Pro plans, you’ll also get access to a free Content Delivery Network (CDN) to speed up page delivery across the globe.
There are other ways that you can improve your site speed. For instance, you can optimize your images and reduce image and text sizes. You can also minimize resources like JavaScript and CSS, and delete outdated or unused plugins.
Provide Clear Navigation Design
It’s important that your navigation menu design is simple and intuitive to help users find what they’re looking for. With this in mind, you can make your top-level items accessible from every web page.
Typically, these items then expand into dropdown menus. However, you’ll want to avoid filling dropdown menus with too many pages. Instead, your menus should be scannable to help users navigate your site quickly.
Mega menus are an excellent option if you’ve got lots of pages on your website:
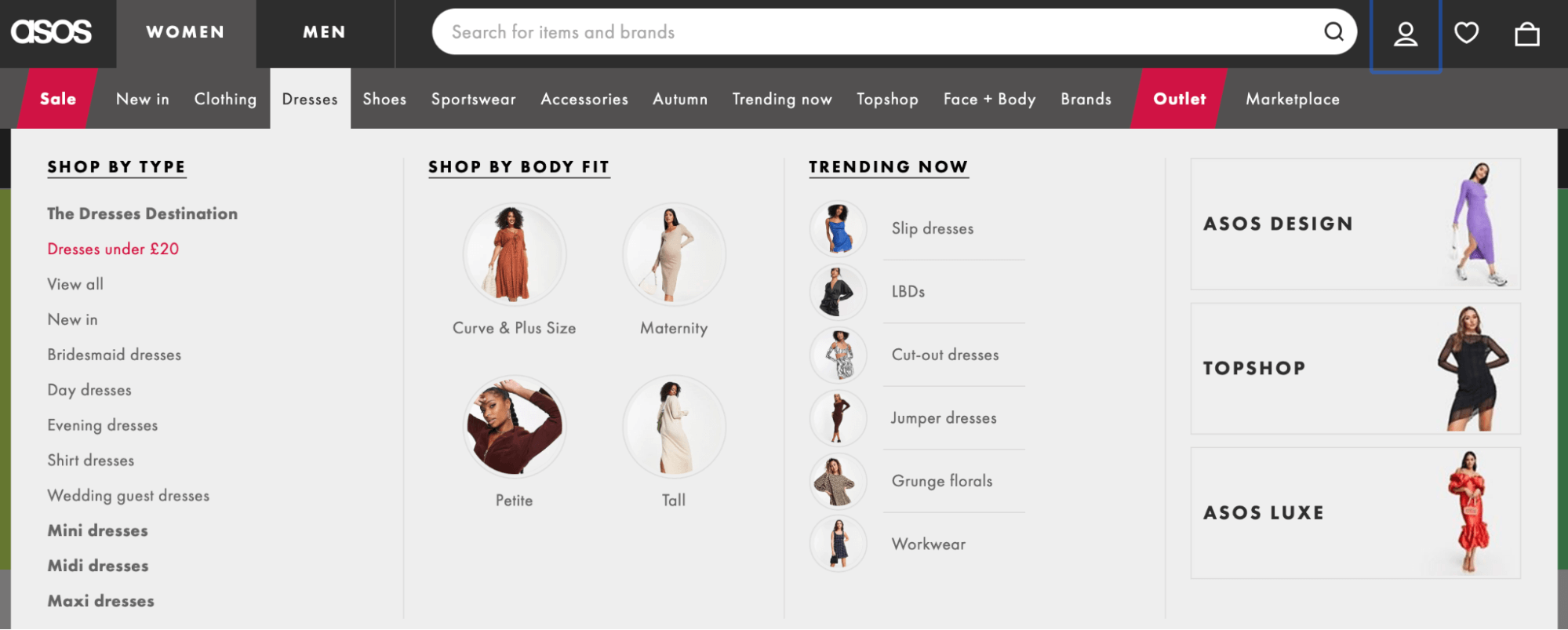
As a result, you can make all your pages visible and accessible from one place. This can help boost your User Experience (UX) and improve user engagement.
And since search engines also use your navigation menu to help understand and ranking your content, clarity and organization matter quite a bit here!
Delete Old Pages
What, delete pages?!
While this may seem counterintuitive, having older, outdated pages on your site still get indexed by Google and wastes what is called your “crawl budget.”
Crawl budget refers to the maximum number of pages a search engine can crawl. This number is determined by several factors including site speed. You can maximize crawlability by cleaning up your website. For instance, you can update existing content or delete pages that are no longer relevant.
This shouldn’t affect your search engine rankings, as long as you target pages that don’t attract much traffic. Also, you can afford to lose pages that contain duplicate content or those with poor link equity. Additionally, it’s a good idea to check that there aren’t any backlinks directing visitors to your deleted pages since this will return a 404 error.
Create an SEO-Friendly Website Structure
As a website owner, one of your main goals is to get more visitors. An excellent way to do this is to improve your search ranking. However, with so much competition, it can be difficult to do.
Fortunately, you can create an SEO-friendly website structure to make your web pages more visible. For example, you can create a simple hierarchy, consisting of pillar pages and subcategories. You can also implement an internal linking strategy, get rid of old content, and optimize your URLs.
At DreamHost, we provide a powerful SEO marketing service to help you rank higher in search engines. You’ll get access to a dedicated team of experts, monthly reports, and excellent optimization strategies including market targeting and PR backlinking. Schedule a free consultation to get started today!
Search Engine Optimization Made Easy
We take the guesswork (and actual work) out of growing your website traffic with SEO.
